Supply Chain vs. Procurement: Key Differences Explained
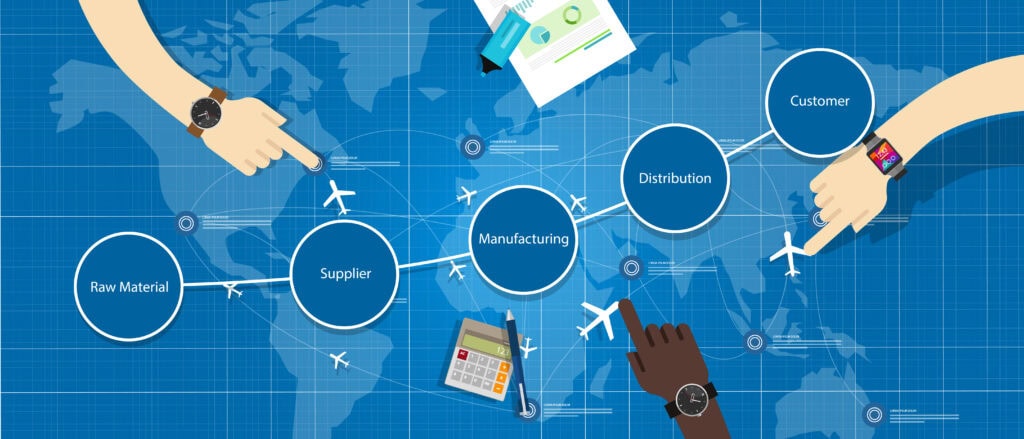
There are critical roles and differences between supply chain and procurement within the commercial shipping industry. Understanding these functions is vital for managing operations efficiently and ensuring organizational success.
Supply chain and procurement play pivotal roles in the success of commercial shipping. Supply chain management involves sourcing raw materials to deliver products to consumers.
It integrates various aspects such as inventory management, logistics providers, and quality assurance, ensuring that every component of the company’s supply chain operates seamlessly to meet customer demands and maintain operational efficiency.
Procurement focuses on acquiring goods and services necessary for a company’s business model. This involves evaluating supplier capabilities, negotiating supplier contracts, and managing procurement processes to achieve cost savings while ensuring the desired quality and timely delivery of goods.
Supply chain management procurement and procurement knowledge is essential for anyone looking to enhance their business operations in the commercial shipping industry.
What is the difference between procurement and supply chain? What is procurement in supply chain? What is procurement supply chain management? This blog will answer those questions. We will also discuss procurement and supply chain news and procurement and supply chain solutions. If you’re looking for information about a procurement operating model or considering a new procurement operating model, or want to better understand procurement capabilities, read on.
Supply Chain Explained
Supply chains represent the comprehensive framework of how supply chain management encompasses all the steps in getting a product from its initial concept to the customer’s hands. It includes every phase, from sourcing the raw materials required to create the product through production to delivering the final goods to the consumer.
At its core, a supply chain involves various participants, including producers, vendors, warehouses, transportation companies, distribution centers, and retailers.
Every element of the supply chain is interconnected, ensuring that each participant, activity, and resource works cohesively to streamline the process. Information flows continuously among all entities to facilitate smooth operations and timely adjustments based on dynamic market demands and customer needs.
Supply Chain Management Explained
Supply chain management (SCM) involves the meticulous oversight of all activities within the supply chain to elevate customer value and secure a sustainable competitive advantage. It integrates significant components like logistics, operations management, and the flow synchronization between the demand and reliable supply chains across different firms.
Effective supply chain management ensures that each supply chain segment collaboratively supports the others, enhancing operational efficiency and optimizing the production cycle.
Key aspects of supply chain management include inventory control, quality assurance, and cost management.
Managers work to maintain optimal inventory levels to meet customer demand while minimizing the costs of overstocking. They also strive for the highest quality in sourcing materials, production processes, and final outputs to prevent issues with defective or unwanted products.
Additionally, by analyzing market trends and maintaining robust supplier relationships, supply chain managers enhance the responsiveness and reliability of the supply chain, ultimately leading to greater customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Procurement Explained
Procurement is a fundamental aspect of the supply chain management process, focusing on acquiring goods and services necessary to fulfill business operations. It involves a series of strategic processes that ensure a company secures the essential resources required to operate effectively and efficiently.
Here are the key elements of the procurement process:
- Vendor Selection: Procurement teams evaluate potential suppliers based on cost, quality, and reliability to find the best matches for the company’s needs.
- Contract Negotiation: Negotiating favorable terms that benefit both the company and the supplier is crucial. This includes pricing, delivery schedules, and payment terms, ensuring timely delivery and cost-efficiency.
- Payment Terms Establishment: Setting clear payment terms is vital for managing cash flow and maintaining good supplier relationships, which is essential for responsive supply chain operations.
- Quality Control Measures: Procurement involves stringent quality checks to ensure that all purchased goods and services meet the desired standards, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Supplier Relationship Management: Maintaining strong supplier relationships ensures a reliable supply chain and can lead to better terms and innovations that benefit both parties.
Key Differences Between Supply Chain and Procurement
Understanding the roles of supply chain and procurement managers is essential for optimizing commercial shipping operations. These functions, while related, target different aspects of business strategy and management.
Procurement Focuses on Acquisition
Procurement, a critical function in the overall supply chain process, is crucial for acquiring the goods and services a business needs to function. It involves strategically selecting suppliers, negotiating contracts, and managing orders to minimize costs and ensure resource quality and timely delivery.
Effective procurement management is key to maintaining reliable supplier relationships and a steady resource flow through its procurement processes, external suppliers, and teams.
Supply Chain Management Orchestrates Flow
In contrast, supply chain management (SCM) ensures the smooth flow of these goods from suppliers to customers. This includes managing logistics, overseeing production, and scheduling to meet demand, focusing on enhancing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The supply chain manager is pivotal in integrating supply chain processes across the network to improve the entire supply chain.
Coordination vs. Strategic Sourcing
While the procurement manager strategically sources and acquires goods, SCM coordinates the broader activities that move these goods to market, focusing on long-term production and distribution planning. Supply chain strategies often involve comprehensive supply chain management processes encompassing every aspect of the system.
Impact on Customer Satisfaction
SCM directly affects customer satisfaction by managing delivery times and product quality through quality control and responsive supply chain strategies.
Procurement indirectly impacts satisfaction by securing quality inputs at reasonable prices, influencing the supplier’s final product’s cost and quality through contract management and negotiation.
Resource Utilization and Technology
SCM optimizes resources across the entire supply chain to reduce waste and improve efficiency, utilizing advanced technologies to enhance process visibility and coordination. Procurement uses technology to streamline functions, ensuring cost-effective purchasing and strong supplier relations.
Flexibility and Adaptability
Supply chain management requires flexibility and adaptability to respond to market changes, demand fluctuations, and logistical challenges. This dynamic approach allows businesses to adjust their operations quickly to avoid disruptions and meet market demands efficiently.
In contrast to supply chain teams, procurement focuses on establishing and maintaining terms that secure resource availability but may not change as frequently.
Risk Management and Mitigation
Supply chain management involves comprehensive risk management, identifying potential disruptions in the supply chain—from supplier failures to transportation issues—and devising strategies to mitigate these risks. This proactive approach by supply chain professionals is essential to maintain continuous operations and meet customer demands consistently.
While procurement professionals are focused on acquiring goods and services, procurement also plays a crucial role in risk management by ensuring supplier diversity and maintaining robust relationships.
This helps mitigate risks associated with supplier dependency and ensures alternative sources are available if primary suppliers encounter problems. This strategic aspect of procurement is vital for stabilizing the supply base and ensuring resource availability even during market or operational challenges.
When Each Is Used
In the business landscape, the emphasis on procurement or a comprehensive supply chain strategy can vary significantly depending on market research and the industry’s specific needs and challenges.
Procurement Focus
Industries such as construction or manufacturing often prioritize procurement. For these sectors, the ability to acquire high-quality raw materials at favorable prices directly impacts production quality and cost-effectiveness.
Example:
A construction company relies heavily on the timely procuring cement, steel, and lumber. Delays or increased costs in acquiring these materials can lead to project overruns and increased expenses, affecting the overall profitability.
Supply Chain Strategy
On the other hand, industries like pharmaceuticals and food and beverages require a robust supply chain strategy. These industries must manage stringent regulatory compliance, storage conditions, timely distribution, and risk management across the supply chain.
Example:
A pharmaceutical company must ensure that drugs are stored and transported at controlled temperatures to maintain efficacy, necessitating a sophisticated supply chain system.
Impact of Procurement Strategies
These enhancements provide a broader perspective on how strategic procurement practices directly contribute to operational success and competitive advantage in both manufacturing and retail sectors.
Manufacturing:
- Procurement strategies in manufacturing focus on sourcing raw materials that meet specific quality standards while being cost-effective.
- Effective procurement strategies can lead to cost savings, which is critical in price-competitive markets.
- Strong relationships with suppliers ensure reliable material flow, crucial for maintaining production schedules without interruption.
Retail:
- Retail sectors emphasize procuring goods that meet consumer trends and preferences, which requires a dynamic approach to sourcing.
- Cost efficiency in procurement helps maintain competitive pricing in retail.
- The ability to quickly adapt to changing supplier landscapes or product trends is crucial in influencing procurement policies.
Contrast with E-commerce
- E-commerce industries thrive on an efficient supply chain strategy that integrates technology to manage various operations, from inventory management to delivery and customer satisfaction.
- The focus is on logistics, warehousing, inventory control, and the ability to deliver products promptly to meet customer expectations.
- Supply chain efficiencies can significantly enhance customer experience by reducing shipping times and costs. This is crucial for maintaining a competitive advantage in a market driven by consumer satisfaction and loyalty.
Conclusion
Throughout this discussion, we have elucidated the critical roles and differences between supply chain and procurement within the commercial shipping industry. Understanding these functions is vital for managing operations efficiently and ensuring organizational success.
Supply chain management involves overseeing the entire process, from sourcing raw materials to delivering the final product, emphasizing the importance of a seamless flow and coordination across various stages of the supply chain network.
On the other hand, the procurement function focuses on strategically acquiring goods and services, negotiating contracts, and managing supplier relationships to support the organization’s objectives and ensure cost efficiency.
With this knowledge, you can better appreciate how these strategic areas influence business operations and contribute to overall customer satisfaction and company performance.
